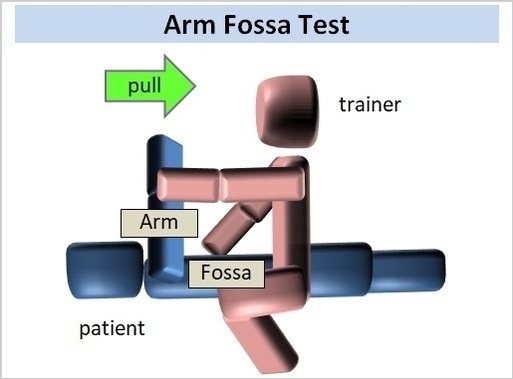
S.O.T by "Arm Fossa Test"
1.Importance of Arm Fossa Test
temporary stressThe Arm Fossa Test, as the name suggests, is a reflex test that combines patient's Arm with Fossa.
This technique can be applied to a wide range of conditions such as sacroiliac joint unbalance, internal organ fatigue, and allergic reactions.
The brain sends minute electrical signals through nerves to move muscles and internal organs.
In the test, stress give to the reflex points of these fossa intentionally . The results are compared before and after the stress give to check if there is any change in arm's reflexes (disturbance of electrical signals).
For example, to check small intestine condition, a temporary finger stress give to patient's navel.
| arm reflexes | judge | |
| temporary stress | No change | No problem |
| change | Suspected fatigue, disease, or disability |
Although the test method is different, the response is similar to that of the O-Ring Test, which uses opening and closing of patient's fingers.
・Exploring the correct S.O.T position
The corrective position to aim for in S.O.T is as follows.
| № | Part | Position | Test |
| 1 | Sacroiliac joint | 4 points on the left, right, upper and lower sides are equal | 〇 |
| 2 | Muscles | No delay in reflexes, no change in strength | 〇 |
| 3 | Internal organs | 〇 | |
| 4 | Pelvis | Pelvic twitch can be relieved | ー |
| 5 | The height of ilium is aligned on both sides | ー |
Pelvis can be checked visually, but sacroiliac joints, muscles and internal organs are difficult to that.
Therefore, the Arm Fossa Test is used to check the correct position of those areas that cannot be checked visually.
However, if autonomic nervous system disturbance are strong, the Arm Fossa Test results may be in error. Be careful if the reflexes are strong or if there is an overall variation.
2.Arm Fossa Test Procedure
Arm Fossa Test In the "Arm" part of , arm positioning is important.
When the command "keep your arm in the same position" is transmitted from brain to arm, your arm automatically adjusts the force of muscles and records the information to maintain the position unconsciously.
Arm Fossa Test technique is based on this unconscious recording.
If patient's arm is not relaxed or the angle of arm is slanted, the test results will not be correct and errors will occur.
| 対象 | 手順 | |
| (1) | patient | Turn palms inward, do not clench fist. |
| (2) | patient | Angle arm at 90 degrees and extend elbow. |
| (3) | trainer | Hold patient's wrist |
・Check inguinal ligament
Along iliac, apply a finger's worth of pressure to the fossa of inguinal ligament point.
| 部位 | 備考 | |
| sacroiliac joint | inguinal region area (right), upper and lower 2 places | left, right, up and down 4 locations |
| inguinal region area (left), upper and lower 2 places |
・Check internal organs
Apply one finger's worth of pressure to the fossa of internal organ point.
Note that only the autonomic reflexes are reversed.
| 部位 | 位置 | 反転 | |
| Cardio-pulmonary | heart | under clavicle | ー |
| coronary artery | sternum(left) | ||
| lung | center clavicle | ||
| Nerve | autonomic nerves | thymus | 〇 |
| Liver function | liver | 10th rib(right) under clavicle(right) | ー |
| gallbladder | on the gallbladder | ||
| Gastrointestine | stomach | on the stomach | ー |
| pancreas | 10th rib(left) | ||
| small intestine | navel | ||
| large intestine | rectum | ||
| reproductive | Uterus・Ovaries | on the Uterus or Ovaries | ー |
| Prostate | male genitalia |
・Check muscles
Pressure is applied to the affected area.
These reflexes are tested on a joint or muscle parts rather than a fixed point.
Pull patient arm while applying pressure stress to his fossa.
If it is a normal reflex, his arm retains its original strength and the +/- is zero.
If the reflex is negative, his arm will not hold its position, the reflex will be delayed, or it will respond to + side.
| 対象 | 手順 | |
| (1) | trainer | Apply pressure to the fossa of inguinal ligament |
| (2) | patient | Pull patient arms toward his head without bending |
| (3) | trainer | Check the changes before and after applying pressure. |
| (4) | trainer | (1)~(3) repeat that 4 locations in inguinal ligament, top, bottom, left and right |
| (5) | trainer | If there is a change in 1 or more of 4 points, the patient is eligible for S.O.T. |
3.Points to grasp your condition
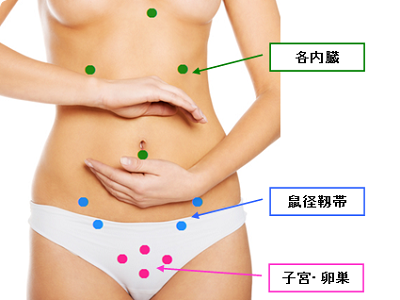
Assessing the condition of your body is the basic technique of S.O.T.
Reflexes do not always have to be strong.
The basic balance appear that during recovery the response is weakness and during action it is strong.
For this reason, the ideal situation is to have a balance of +/- zero.
If your reaction is too strong, you will expend extra energy, and if your reaction is too weak, you will not be able to act adequately.
3-1 Inguinal points
This is the basic point for S.O.T, and 4 points are checked: left, right, upper and lower groin.
Those position where 4 points are evenly is the position that stabilizes the body and places the least burden on sacroiliac joint.
3-2 Internal organs point
Each internal organ, such as stomach, intestines, heart, and liver, has its own checkpoint.
If there is an accumulation of waste, load, etc. in internal organs, the reflexes will late
In addition, internal organs have a tendency to help each other, supporting that are not in good shape. This means that what appears to be a stable condition is actually an unstable condition.
For example, when stomach is tired, intestines will work harder than usual to follow up. However, it is overwork by normal operating rate.
3-3 Reproductive organs points
Women use pubic bone as a fulcrum and measure the point of the uterus and ovaries from there with their fingers.
Men use pubic bone as a fulcrum and measure the point of the entire palm of the hand over male organ.
The female genitals, in particular, are thought to have lost their role after menopause, but this is not true.
It is likely that they continue to contribute in some way throughout life, for example by maintaining lymphatic circulation.